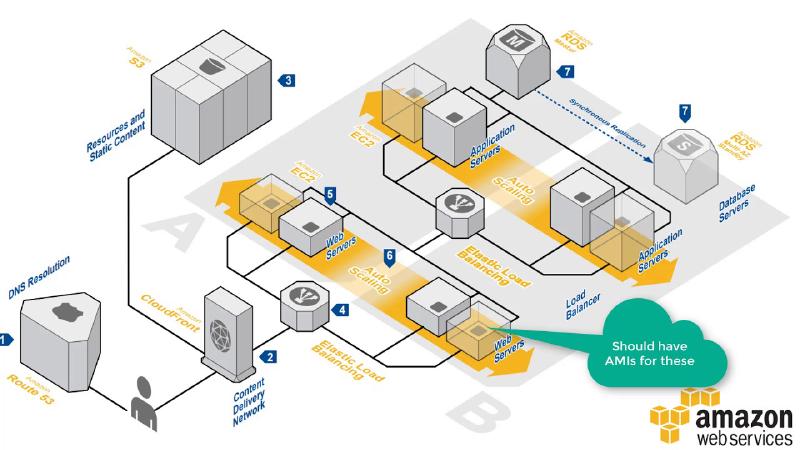
This time I’ll be using an environment with a Load Balancer and an Autoscaling Group, which is a more complex architecture than the previous one.
We’ll have the following resources deployed with this procedure:
- 1 VPC
- 2 Subnets
- 1 Internet Gateway
- 1 Route Table (with a default route and an association)
- 2 Security groups
- 1 Key Pair
- 1 EC2 Instance
- 1 Launch Configuration
- 1 ELB
- 1 ASG
- 2 Autoscaling Policies
- 2 Cloudwatch Metric Alarms
It’s a very simple and you can build on top of it according to your needs, like the previous infrastructure. The code will be organized in the following structure:
- main.tf: resource declaration
- providers.tf: aws provider configuration
- outputs.tf: output declaration
- datasources.tf: we’ll get the AMI information here
- userdata.tpl: script to be executed on first boot
I’ll put the code first and then explain the most important parts. Let’s start with providers.tf:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 3.0"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
shared_credentials_file = "/home/mando/.aws/credentials"
profile = "mando"
region = "us-east-1"
}
|
Terraform requires credentials to access your account on AWS. You can choose different approaches for that, like putting the keys directly instad of pointing to a credentials file. Although that works and might even be easier, you’ll probably have your code pushed into a git repository which would then expose the keys. More information on how to configure the provider can be found here -> Docs overview | hashicorp/aws.
Now for the main.tf:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
| resource "aws_vpc" "mando_vpc" {
cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"
enable_dns_hostnames = true
tags = {
Name = "Mando VPC"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "mando_public_subnet_us_east_1a" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.mando_vpc.id
cidr_block = "10.10.1.0/24"
availability_zone = "us-east-1a"
tags = {
Name = "Mando Public Subnet US-East 1a"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "mando_public_subnet_us_east_1b" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.mando_vpc.id
cidr_block = "10.10.2.0/24"
availability_zone = "us-east-1b"
tags = {
Name = "Mando Public Subnet US-East 1b"
}
}
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "mando_vpc_igw" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.mando_vpc.id
tags = {
Name = "Mando VPC - Internet Gateway"
}
}
resource "aws_route_table" "mando_vpc_public" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.mando_vpc.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.mando_vpc_igw.id
}
tags = {
Name = "Public Subnets Route Table for Mando VPC"
}
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "mando_vpc_us_east_1a_public" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.mando_public_subnet_us_east_1a.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.mando_vpc_public.id
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "mando_vpc_us_east_1b_public" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.mando_public_subnet_us_east_1b.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.mando_vpc_public.id
}
resource "aws_security_group" "allow_http" {
name = "allow_http"
description = "Allow HTTP inbound connections"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.mando_vpc.id
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
Name = "Allow HTTP Security Group"
}
}
resource "aws_key_pair" "mando_key" {
key_name = "mando-key"
public_key = "ssh-rsa AAAABACH3L0Lc2EAAAADAQAPNCDAgQDELie/jIMM8uno12enId2YTmTjK1OGZJtTJFoSPdXIwn79qpZYQ3WXL8PlI/8dqFyGXvQj5bGJbgEydjSYVHFXFhPr4sdKcjguWbu895EjK2DgalcYuC1+6jBbFxiodoObsc+84m81+BACH3L0LQU3cm/rNKufrh6d21jIe4sQVul+WzJ9E8aPk34rPmRPgjYvh1T/P2hdgiUyJmKqOtDYwpokDRad+3W+iwGfoBACH3L0LoCWJ2rYzz6j80FKoiHm9cnSXvErezT7aAdenVzY3nEE4ylnHWVUdmzXN7IbCSLsDV3sdn0+c5E6oDX2/k1VwtSQ8TrUblM7AdpuB4ADniUSYvLqjd/NBIiHODzV6qZxXqoltVTsrTpbCWf1A063PBACH3L0L/F3mxBihWRAKfD1iqqfMXmYvAPosOkJ3u1yuwy/eCi6Q3SmA5n0vBSVKmYdUB9yQdAimWcUqabRzXLz+g8BrUxCBHwOf4+IZAp2AseJeoDQs0aqMwybr/k= mando" # replace with your key
}
resource "aws_launch_configuration" "web" {
name_prefix = "web-"
image_id = data.aws_ami.server_ami.id
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = aws_key_pair.mando_key.id
security_groups = [aws_security_group.allow_http.id]
associate_public_ip_address = true
user_data = file("userdata.tpl")
lifecycle {
create_before_destroy = true
}
}
resource "aws_security_group" "elb_http" {
name = "elb_http"
description = "Allow HTTP traffic to instances through Elastic Load Balancer"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.mando_vpc.id
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
Name = "Allow HTTP through ELB Security Group"
}
}
resource "aws_elb" "web_elb" {
name = "web-elb"
security_groups = [
aws_security_group.elb_http.id
]
subnets = [
aws_subnet.mando_public_subnet_us_east_1a.id,
aws_subnet.mando_public_subnet_us_east_1b.id
]
cross_zone_load_balancing = true
health_check {
healthy_threshold = 2
unhealthy_threshold = 2
timeout = 3
interval = 30
target = "HTTP:80/"
}
listener {
lb_port = 80
lb_protocol = "http"
instance_port = "80"
instance_protocol = "http"
}
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "web" {
name = "${aws_launch_configuration.web.name}-asg"
min_size = 1
desired_capacity = 2
max_size = 4
health_check_type = "ELB"
load_balancers = [
aws_elb.web_elb.id
]
launch_configuration = aws_launch_configuration.web.name
enabled_metrics = [
"GroupMinSize",
"GroupMaxSize",
"GroupDesiredCapacity",
"GroupInServiceInstances",
"GroupTotalInstances"
]
metrics_granularity = "1Minute"
vpc_zone_identifier = [
aws_subnet.mando_public_subnet_us_east_1a.id,
aws_subnet.mando_public_subnet_us_east_1b.id
]
# Required to redeploy without an outage.
lifecycle {
create_before_destroy = true
}
tag {
key = "Name"
value = "web"
propagate_at_launch = true
}
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_policy" "web_policy_up" {
name = "web_policy_up"
scaling_adjustment = 1
adjustment_type = "ChangeInCapacity"
cooldown = 300
autoscaling_group_name = aws_autoscaling_group.web.name
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "web_cpu_alarm_up" {
alarm_name = "web_cpu_alarm_up"
comparison_operator = "GreaterThanOrEqualToThreshold"
evaluation_periods = "2"
metric_name = "CPUUtilization"
namespace = "AWS/EC2"
period = "120"
statistic = "Average"
threshold = "60"
dimensions = {
AutoScalingGroupName = aws_autoscaling_group.web.name
}
alarm_description = "This metric monitor EC2 instance CPU utilization"
alarm_actions = [aws_autoscaling_policy.web_policy_up.arn]
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_policy" "web_policy_down" {
name = "web_policy_down"
scaling_adjustment = -1
adjustment_type = "ChangeInCapacity"
cooldown = 300
autoscaling_group_name = aws_autoscaling_group.web.name
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "web_cpu_alarm_down" {
alarm_name = "web_cpu_alarm_down"
comparison_operator = "LessThanOrEqualToThreshold"
evaluation_periods = "2"
metric_name = "CPUUtilization"
namespace = "AWS/EC2"
period = "120"
statistic = "Average"
threshold = "10"
dimensions = {
AutoScalingGroupName = aws_autoscaling_group.web.name
}
alarm_description = "This metric monitor EC2 instance CPU utilization"
alarm_actions = [aws_autoscaling_policy.web_policy_down.arn]
}
|
Since it is a big file, let’s divide it in parts:
- VPC, subnets, route tables and routes, internet gateway, security group and key pair: the foundation or basic part of the infrastructure;
- Launch Configuration: this is where we define the parameters for the EC2 instances that the Autoscaling Group will launch. It’s very similar to when we deploy a single EC2 instance;
- Elastic Load Balancer: we deploy a security group specifically for the ELB first, and then the ELB itself. We have to specify which subnets, the listener and the health checks we’ll use;
- Autoscaling Group: this is the most important part regarding on how the infrastructure will “behave”, let’s say. We define a minimum, desired and maximum number of instances; specify what is going to be the health check, in this case is ELB so instance availability will be provided by it; then we set some Cloudwatch metrics to provide observability and add tags to identify the instances.
outputs.tf:
1
2
3
| output "elb_dns_name" {
value = aws_elb.web_elb.dns_name
}
|
The only output we have is the DNS name of the ELB, which we’ll need to access it.
userdata.tpl:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| #!/bin/bash
sudo apt -y update &&
sudo apt -y install \
nginx &&
echo "$(curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/local-ipv4)" > /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
sudo systemctl enable nginx
sudo systemctl start nginx
|
This userdata will install nginx on the EC2 instance at the first boot.